無料3V0-22.21サンプル問題で100%カバー率のリアル試験問題(更新された17問あります)
今すぐダウンロード!リアルVMware 3V0-22.21試験問題集テストエンジン試験問題
VMware 3V0-22.21認定試験は、高度なVSphere展開の概念を深く理解する必要がある挑戦的な試験です。候補者は、VSphereネットワーキング、ストレージ、セキュリティ、および自動化に関する知識と理解についてテストされます。認定試験は、複雑なVSPhere環境を設計、実装、および管理する候補者の能力を検証するように設計されています。この認定試験に合格することは、仮想化とクラウドコンピューティングのキャリアを促進したいITプロフェッショナルにとって大きな成果です。
質問 # 10
A new internal network is required to isolate virtual machines for security analysis. The virtual machine (honeypot-01) should reside on a new virtual standard switch with the ability for all traffic on the switch to be monitored.
Add a new virtual switch to accommodate this requirement and configure (honeypot-01) to reside on this switch.
Use the following information to complete this task:
* ESXi host: esxi0la
* Standard Switch: Create a new Standard Switch
* Physical uplink: NO UPLINK
* Network Label: QUARANTINE
* VLAN: none specified
- A. Send us your suggestions.
正解:A
質問 # 11
A vSphere administrator has deployed a new server. The VM will have a workload which is prodApp1 to the following specifications:
* The VM should never have any memory contention while powered on. even if the host that it resides
* Configure the virtual machine for high latency sensitivity.
- A. Send us your suggestions.
正解:A
質問 # 12
Your storage administrator is concerned about a new application being deployed on virtual machine (SIOCVM) in your vSphere 7.x environment.
You've been asked to create and apply a storage policy to make sure that the SIOCVM virtual machine does not exceed 500 IOPS.
Note: Name the Storage Policy 500IOPSLimit
正解:
解説:
Storage I/O Control v2
Storage I/O Control (SIOC) was initially introduced in vSphere 4.1 to provide I/O prioritization of virtual machines running on a cluster of ESXi hosts that had access to shared storage. It extended the familiar constructs of shares and limits, which existed for CPU and memory, to address storage utilization through a dynamic allocation of I/O queue slots across a cluster of ESXi servers. The purpose of SIOC is to address the 'noisy neighbor' problem, i.e. a low priority virtual machine impacting other higher priority virtual machines due to the nature of the application and its I/O running in that low priority VM.
vSphere 5.0 extended SIOC to provide cluster-wide I/O shares and limits for NFS datastores. This means that no single virtual machine should be able to create a bottleneck in any environment regardless of the type of shared storage used. SIOC automatically throttles a virtual machine which is consuming a disparate amount of I/O bandwidth when the configured latency threshold has been exceeded. To allow other virtual machines receive their fair share of I/O bandwidth on the same datastore, a share based fairness mechanism has been created which now is supported on both NFS and VMFS.
vSphere 5.1 introduced a new SIOC feature called Stats Only Mode. When enabled, it doesn't enforce throttling but gathers statistics to assist Storage DRS. Storage DRS now has statistics in advance for new datastores being added to the datastore cluster & can get up to speed on the datastores profile/capabilities much quicker than before.
Another 5.1 feature was Automatic Threshold Computation. The default latency threshold for SIOC is 30ms. Not all storage devices are created equal so this default was chosen as a sort of "catch-all". There are certain devices which will hit their natural contention point much earlier than others, for example All Flash Arrays, in which case the threshold should be lowered by the user. However, manually determining the correct latency can be difficult for users. This gave rise to the need for the latency threshold to get automatically determined at a correct level for each device. Using the I/O injector modeling of SIOC, peak throughput and corresponding latency of a datastore is measured. The latency threshold value at which Storage I/O Control will kick in is then set to 90% of this peak value (by default). vSphere administrators can change this 90% to another percentage value or they can still input a millisecond value if they so wish.
The default latency threshold for SIOC can be reduced to as low as 5ms.
SIOC V1 Overview
SIOC V1 is disabled by default. It needs to be enabled on a per datastore level, and it is only utilized when a specific level of latency has been reached. By default, the latency threshold for a datastore is set to 30ms, as mentioned earlier. If SIOC is triggered, disk shares (aggregated from all VMDKs using the datastore) are used to assign I/O queue slots on a per host basis to that datastore. In other words, SIOC limits the number of IOs that a host can issue. The more VMs/VMDKs that run on a particular host, the higher the number of shares, and thus the higher the number of IOs that that particular host can issue. The throttling is done by modifying the device queue depth of the various hosts sharing the datastore. When the period of contention passes, and latency returns to normal values, the device queue depths are allowed to return to default values on each host.
SIOC V2 Introduction
Before describing SIOC V2, it should be highlighted that SIOC V1 and SIOC V2 can co-exist on vSphere 6.5. This makes it much simpler when considering upgrades, or migrations between versions. With that in mind, SIOC V2 is considerably different from a user experience perspective when compared to V1. SIOCv2 is implemented using IO Filter framework Storage IO Control category. SIOC V2 can be managed using SPBM Policies. What this means is that you create a policy which contains your SIOC specifications, and these policies are then attached to virtual machines.
Creating an SIOC policy based
Creating an SIOC policy is done is exactly the same way as building a storage policy for VSAN or Virtual Volumes. Select the VM Storage Policy from the vSphere client home page, and from there select the option to create a new VM Storage Policy. VM Storage Policies in vSphere 6.5 has a new option called "Common Rules". These are used for configuring data services provided by hosts, such as Storage I/O Control and Encryption.
Use common rules in the VM storage policy
The first step is to click on the check box to enabled common rules. This will then allow you to add components, such as SIOC, to the policy.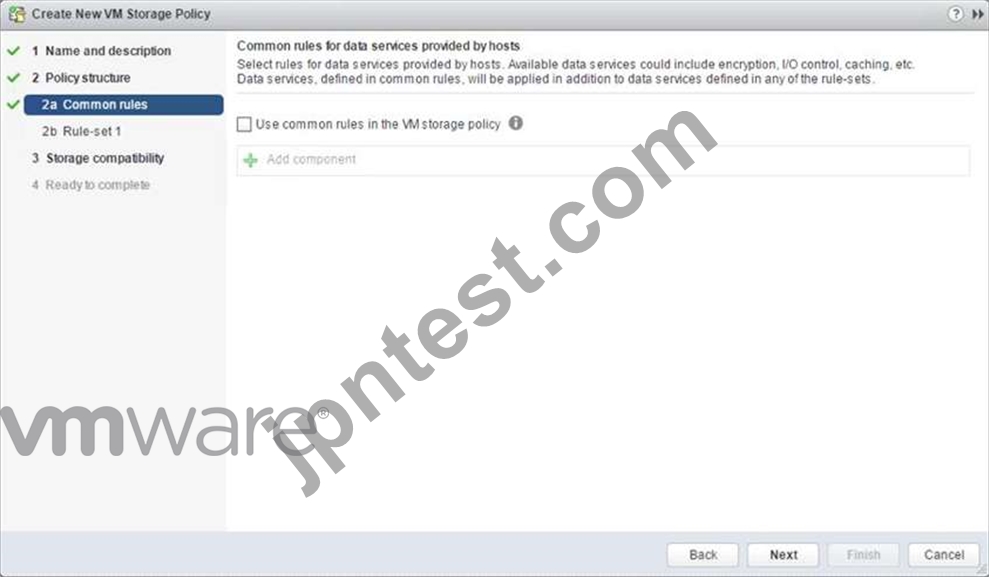
Add Component - Storage I/O Control
In vSphere 6.5, there are two components available for common rules, Encryption and Storage I/O Control. Select Storage I/O Control in this case. Now you can select Normal, High, Low or Custom shares allocation.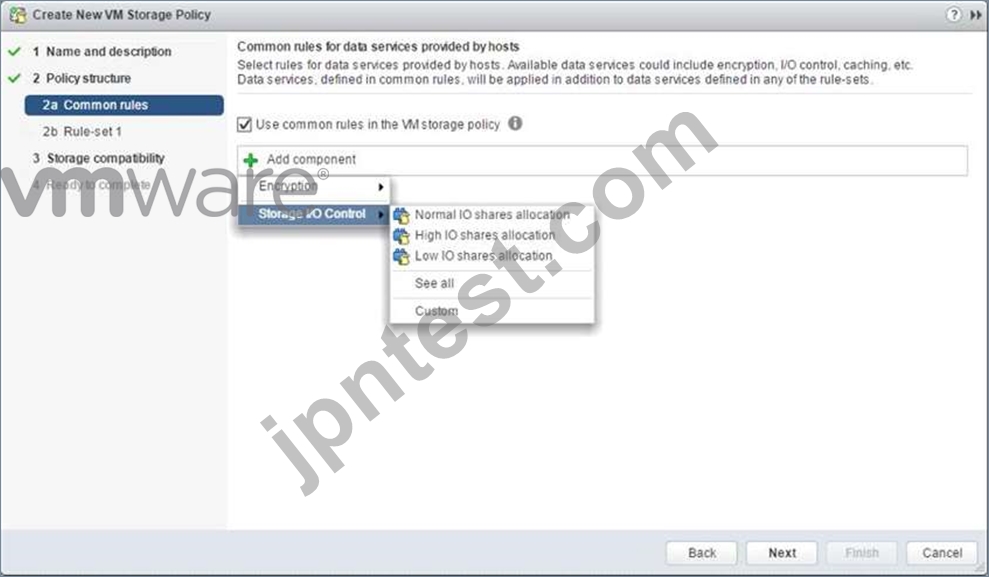
This table describes the different Limits,Shares and Reservations associated with each setting:
HIGH
NORMAL
LOW
Limits
100,000
10,000
1,000
Reservation
100
50
10
Shares
2,000
1,000
500
When the policy has been created, it may be assigned to newly deployed VMs during provisioning,or to already existing VMs by assigning this new policy to the whole VM (or just an individual VMDK) by editing its settings. One thing to note is that IO Filter based IOPS does not look at the size of the IO. For example, there is no normalization so that a 64K IOP is not equal to 2 x 32K IOPS. It is a fixed value of IOPS irrespective of the size of the IO.
Custom Allocation
If neither of the values in the Normal, High, Low allocations is appropriate, there is the ability to create custom settings for these values. In a custom setting, IOPS limit and IOPS reservation are both set to -1, implying unlimited. These may be modified as required.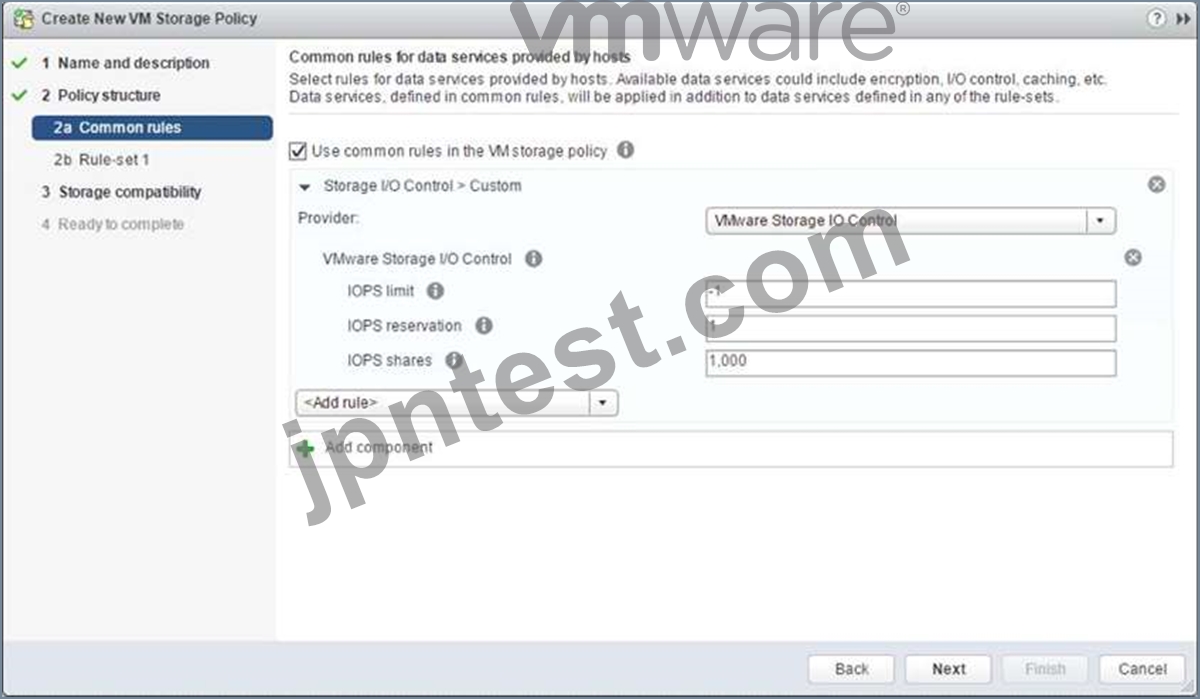
Advanced Options
SchedCostUnit
This is an advanced parameter that was created for SIOC V1 only. SIOC V2 does not have SchedCostUnit implemented. For V1, SchedCostUnit determines the unit size (normalized size) of an IO operation for scheduling, and it is currently a constant value of 32K. This constant value, however, may not satisfy different requirements from different customers. Some customers may want to set this unit size to 4K. Other customers may want to set it up to 256K.
To satisfy these different requirements, SchedCostUnit is now configurable. It defaults to an IO size value of 32K, and allowable values range between 4K to 256K.
The SchedCostUnit dictates how requests are counted. A request with size <= SchedCostUnit counts as a single I/O. Anything greater than SchedCostUnit will be counted as 2 or more requests.
For example, by changing the SchedCostUnit from 32K to 64K, the number of IOPS observed will halve. The size of the IO can be set using the:
"esxcli system settings advanced set -o /Disk/SchedCostUnit -i 65536"
and verified by using the"
"esxcli system settings advanced list -o /Disk/SchedCostUnit"
command. SIOC V2 counts guest IO directly. IOPS will be counted based on IO count, regardless of the IO size.
SchedReservationBurst
When limits are set on VMDKs, requests could have high average latency because the limit was enforced at a high (per request) granularity. This was due to the strict enforcement on a VM getting its share of IOs in interval of 1 second/L, where L is the user specified limit. The issue is more visible in fast storage, such as flash arrays. It was noted that SIOC V2 did not perform well when presented with a "bursty" workload on fast storage.
This SchedReservationBurst setting relaxes that constraint so a VM get its share of IOs at any time during a 1 second window, rather than enforce strict placement of IOs in intervals of 1/L. BURST option is turned-on by default.
SIOC V2 Limitations
In this initial release of SIOC V2 in vSphere 6.5, there is no support for vSAN or Virtual Volumes. SIOC v2 is only supported with VMs that run on VMFS and NFS datastores.
質問 # 13
The security team has decided to follow the VMware-recommended best practices in the vSphere hardening guide.
esxi02b:
Your first task is to create a local user in esxi02b:
* Name: SpecialUser
* Role: Administrator
Your second task is to ensure that SpecialUser is the ONLY user who is able to SSH into esxi02b via Putty.
Your final task is to enforce a strict lockdown on esxi02b.
Your second task is to ensure that SpecialUser is the ONLY user who is able to SSH into esxi02b via Putty.
Your final task is to enforce a strict lockdown on esxi02b.
正解:
解説:
Authentication and authorization govern access. vCenter Single Sign-On supports authentication, which means it determines whether a user can access vSphere components at all. Each user must also be authorized to view or manipulate vSphere objects.
vSphere supports several different authorization mechanisms, discussed in Understanding Authorization in vSphere. The focus of the information in this section is how the vCenter Server permission model works and how to perform user management tasks.
vCenter Server allows fine-grained control over authorization with permissions and roles. When you assign a permission to an object in the vCenter Server object hierarchy, you specify which user or group has which privileges on that object. To specify the privileges, you use roles, which are sets of privileges.
Initially, only the administrator user for the vCenter Single Sign-On domain, [email protected] by default, is authorized to log in to the vCenter Server system. That user can then proceed as follows:
Add an identity source in which users and groups are defined to vCenter Single Sign-On. See the Platform Services Controller Administration documentation.
Give privileges to a user or group by selecting an object such as a virtual machine or a vCenter Server system and assigning a role on that object for the user or group.
質問 # 14
You are doing an audit for vCenter Server vcsa0la s inventory.
On the desktop, you will find a folder named "powercli-question". In the folder, there is a script named "vds-script.psl".
Your colleague needs some help to get it working as expected. Your task is to modify the script so that it exports a list of virtual machines, enables promiscuous mode on PCLI-Portgroup. and exports PCLl-Portgroup.
- A. Send us your suggestions.
正解:A
質問 # 15
The current vSphere environment will be adding new ESXi hosts that will be used to create a QA compute cluster. This cluster should have HA properties specific to the workloads that will be running in it.
In preparation of adding the new hosts, create the new cluster. QA-Cluster in. Datacenter-PROD on vcsa0la.vclass.local with the following HA requirements:
* The cluster should not contain any ESXi hosts or VMs
* Hosts should be monitored.
* VMs should be restarted in the event of a host failure.
* VMs should be restarted if guest heartbeats are not detected.
* In the case of a host becoming isolated, shutdown and restart VMs.
* If there is an All Paths Down event, any affected VMs must be moved to another host.
* Reserve 10% of memory and CPU for failover capacity.
Part 2
You have been given a requirement for a virtual machine to have no downtime when an ESXi host failure occurs. Configure Fault Tolerance on VM1-FT in the PROD-B cluster. Use any compatible secondary host and datastore. Configure the following advanced cluster settings. Use SAN01 as the storage during configuration.
das.isolationaddress0 172.20.10.11
dass.igoreRedundantNetWarining true
Note: ignore any related host, customer, or bandwidth warnings as long as fault tolerance is configured and VM1-FT is running.
- A. Send us your suggestions.
正解:A
質問 # 16
You have been asked to create a new datastore for the Production cluster; however, the ESXi host esxi02a is not able to add the datastore. Your storage team has determined that there is nothing incorrect with the storage presentation.
Troubleshoot why host esxi02a is not able to create the datastore. Add the datastore to the host once the proper configuration has been applied, and then reboot the host!
Use the following information to complete this task;
* ESXi host: esxi02a
* Datastore Name: new_datastore
* Datastore target: iSCSI Target
* Datastore LUN: 4
* Reboot the host
正解:
解説:
Cannot create a new datastore from vCenter Server or directly from the vSphere Client Creating a new datastore fails The Add Storage Wizard reports the error: An error occurred during host configuration. Call "HostDatastoreSystem.QueryVmfsDatastoreCreateOptions" for object "ha-datastoresystem" on ESXi "xxx.xxx.xxx.xx" failed. An internal error occurred in the vsphere client.
Cause
This issue may occur if:
The size of the LUN is more than 2TB - 512 bytes. The maximum LUN size in vSphere 4 is 2TB - 512 bytes. For more information on this limitation, see Troubleshooting a LUN that is extended in size past the 2TB/2047GB limit (1004230).
The LUN being presented was used as an RDM earlier and does not have a valid partition table.
The LUN being presented was used as a disk device on an other operating system and does not have a valid partition table.
The LUN contains a GPT partition that cannot be removed.
Resolution
To prevent this issue:
Ensure that the LUN size is less than 2TB - 512 bytes or 2047GB. If the LUN is larger then 2TB - 512 bytes, delete it from your Storage Array and recreate it with a size less than the 2TB - 512 bytes limit.
If the disk was used by another operating system in the past (I.E.: it was an RDM, or Linux, FreeBSD, or other filesystem) or contains a GPT partition, you must delete the partition information.For more information
質問 # 17
......
最新3V0-22.21テスト問題集を試そう!更新されたVMware試験が合格できます:https://www.jpntest.com/shiken/3V0-22.21-mondaishu
