8010無料認定試験材料はこちらの242問題
リアル8010は100%カバー率リアル試験問題を試そう!
PRMIA 8010認定は、グローバルに認められ、金融機関によって高く評価されています。これは卓越性の証であり、候補者がオペレーショナルリスクマネジメントのベストプラクティスに取り組んでいることを示しています。認定は候補者に競争上の優位性を提供し、新しいキャリアの機会を開拓することができます。全体として、PRMIA 8010認定は、オペレーショナルリスクマネジメントに関わるプロフェッショナルが、この分野での知識とスキルを向上させたいと考えている場合には優れた投資となります。
質問 # 139
Which of the following are valid approaches for extreme value analysis given a dataset:
I. The Block Maxima approach
II. Least squares approach
III. Maximum likelihood approach
IV. Peak-over-thresholds approach
- A. I and IV
- B. II and III
- C. All of the above
- D. I, III and IV
正解:A
解説:
Explanation
For EVT, we use the block maxima or the peaks-over-threshold methods. These provide us the data points that can be fitted to a GEVdistribution.
Least squares and maximum likelihood are methods that are used for curve fitting, and they have a variety of applications across risk management.
質問 # 140
Which of the following formulae correctly describes Component VaR. (p refers to the portfolio, and i is the i-th constituent of the portfolio. MVaR means Marginal VaR, and other symbols have their usual meanings.)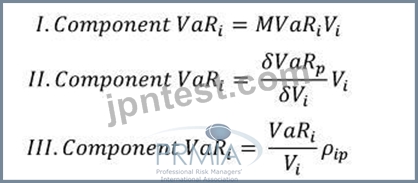
- A. I
- B. III
- C. I and II
- D. II
正解:C
解説:
Explanation
The first two formulae describe component VaR. The last formula is the formula for Marginal VaR. Therefore I and II is the correct answer.
Component VaR is a VaR decomposition technique that allows the total VaR for a portfolio to be broken down and attributed to the components of a portfolio. The total of the component VaR for each constituent of a portfolio is equal to the VaR for the portfolio. This property is extremely useful as opposed to the standalone VaR for each constituent taken alone as it can be used for allocating trading budgets.
質問 # 141
Which of the following cannot be used as an internal credit rating model to assess an individual borrower:
- A. Distance to default model
- B. Altman's Z-score
- C. Logit model
- D. Probit model
正解:A
解説:
Explanation
Altman's Z-score, the Probit and the Logit models can all be used to assess the credit rating of an individual borrower. There is no such model as the 'distance todefault model', and therefore Choice 'a' is the correct answer.
質問 # 142
Concentration risk in a creditportfolio arises due to:
- A. Issuers of the securities in the portfolio being located in the same country
- B. A high degree of correlation between the default probabilities of the credit securities in the portfolio
- C. Independence of individual default losses for the assets in the portfolio
- D. A low degree of correlation between the default probabilities of the credit securities in the portfolio
正解:A
解説:
Explanation
Concentration risk in a credit portfolio arises due to a high degree of correlation betweenthe default probabilities of the issuers of securities in the portfolio. For example, the fortunes of the issuers in the same industry may be highly correlated, and an investor exposed to multiple such borrowers may face 'concentration risk'.
A low degreeof correlation, or independence of individual defaults in the portfolio actually reduces or even eliminates concentration risk.
The fact that issuers are from the same country may not necessarily give rise to concentration risk - for example, a bank withall US based borrowers in different industries or with different retail exposure types may not face practically any concentration risk. What really matters is the default correlations between the borrowers, for example a lender exposed to cement producersacross the globe may face a high degree of concentration risk.
質問 # 143
A bank holds a portfolio ofcorporate bonds. Corporate bond spreads widen, resulting in a loss of value for the portfolio. This loss arises due to:
- A. Liquidity risk
- B. Counterparty risk
- C. Credit risk
- D. Market risk
正解:D
解説:
Explanation
The difference between the yields oncorporate bonds and the risk free rate is called the corporate bond spread.
Widening of the spread means that corporate bonds yield more, and their yield curve shifts upwards, driving down bond prices. The increase in the spread is a consequence of the market risk from holding these interest rate instruments, which is a part of market risk. If the reduction in the value of the portfolio were to be caused by a change in the credit rating of the bonds held, it would have been a loss arising due to credit risk.
Counterparty risk and liquidity risk are not relevant for this question. Therefore Choice 'c' is the correct answer.
質問 # 144
Which of the following steps are required for computing the aggregate distribution for a UoM for operational risk once loss frequency and severity curves have been estimated:
I. Simulate number of losses based on the frequency distribution
II. Simulate the dollar value of the losses from the severity distribution III. Simulate random number from the copula used to model dependence between the UoMs IV. Compute dependent losses from aggregate distribution curves
- A. All of the above
- B. None of the above
- C. I and II
- D. III and IV
正解:C
解説:
Explanation
A recap would be in order here: calculating operational risk capital is a multi-step process.
First, we fit curves to estimate the parameters to our chosen distribution types for frequency (eg, Poisson), and severity (eg, lognormal). Note that these curves are fitted at the UoM level - which is the lowest level of granularity at which modeling is carried out. Since there are many UoMs, there are are many frequency and severity distributions. However what we are interested in is the loss distribution for the entire bank from which the 99.9th percentile loss can be calculated. From the multiple frequency and severity distributions we have calculated, this becomes a two step process:
- Step 1: Calculate the aggregate loss distribution for each UoM. Each loss distribution is based upon and underlying frequency and severity distribution.
- Step 2: Combine the multiple loss distributions after considering the dependence between the different UoMs. The 'dependence' recognizes that the various UoMs are not completely independent, ie the loss distributions are not additive, and that there is a sortof diversification benefit in the sense that not all types of losses can occur at once and the joint probabilities of the different losses make the sum less than the sum of the parts.
Step 1 requires simulating a number, say n, of the number of losses that occur in a given year from a frequency distribution. Then n losses are picked from the severity distribution, and the total loss for the year is a summation of these losses. This becomes one data point. This process of simulating the number of losses andthen identifying that number of losses is carried out a large number of times to get the aggregate loss distribution for a UoM.
Step 2 requires taking the different loss distributions from Step 1 and combining them considering the dependence between the events. The correlations between the losses are described by a 'copula', and combined together mathematically to get a single loss distribution for the entire bank. This allows the 99.9th percentile loss to be calculated.
質問 # 145
Under the contingent claims approach to credit risk, risk increases when:
I. Volatility of the firm's assets increases
II. Risk free rate increases
III. Maturity of the debt increases
- A. I, II and III
- B. II and III
- C. I and III
- D. I and II
正解:C
解説:
Explanation
Under the contingent claims approach, credit risk is evaluated as the value of the put on the firm's assets with a strike price equal to the face value of the debt and maturity equal to the maturity of the obligation. The Black Scholes model can then be used to value the put, and therefore an increase in volatility and the time to expiry (ie maturity) will increase the value of the debt. An increase in the risk free rate will actually reduce the value of the put, therefore statements I and III are correct and Choice 'b' is the correct answer.
質問 # 146
If the marginal probabilities of default for a corporate bond for years 1, 2 and 3 are 2%, 3% and 4% respectively, what is the cumulative probability of default at the end of year 3?
- A. 9.58%
- B. 91.26%
- C. 9.00%
- D. 8.74%
正解:D
解説:
Explanation
Marginal probabilities of default are the probabilities for default for a given period, conditional on survival till the end of the previous period. Cumulative probabilities of default are probabilities of default by a point in time, regardless of when the default occurs. If the marginal probabilities of default for periods 1, 2... n are p1, p2...pn, then cumulative probability of default can be calculated as Cn = 1 - (1 - p1)(1-p2)...(1-pn). For this question, we can calculate the probability of default for year 3 as =1 - (1-2%)*(1-3%)*(1-4%) = 8.74%
質問 # 147
An error by a third party service provider results in a loss to a client that the bank has to make up. Such as loss would be categorized per Basel IIoperational risk categories as:
- A. Execution delivery and process management
- B. Business disruption and process failure
- C. Abnormal loss
- D. Outsourcing loss
正解:A
解説:
Explanation
Choice 'a' is the correct answer. Refer to the detailed loss event type classification under Basel II (see Annex 9 of the accord). You should know the exact names of all loss event types, and examples of each.
質問 # 148
For a back office function processing 15,000 transactions a day with an error rate of 10 basis points, what is the annual expected loss frequency (assume 250 days in a year)
- A. 0
- B. 0.06
- C. 1
- D. 2
正解:D
解説:
Explanation
An error rate of 10 basis points means the number of errors expected in a day will be 15 (recall that 100 basis points = 1%). Therefore the total number of errors expected in a year will be 15 x250 = 3750. Choice 'a' is the correct answer.
質問 # 149
What does a middle office do for a trading desk?
- A. Reconciliations
- B. Risk analysis
- C. Transaction data entry
- D. Operations
正解:B
解説:
Explanation
The 'middle office' is a term used for the risk management function, thereforeChoice 'd' is the correct answers.
The other functions describe what the 'back office' does (IT, accounting). The 'front office' includes the traders.
質問 # 150
If the default hazard rate for a company is 10%, and the spread on its bondsover the risk free rate is 800 bps, what is the expected recovery rate?
- A. 8.00%
- B. 20.00%
- C. 0.00%
- D. 40.00%
正解:B
解説:
Explanation
The recovery rate, the default hazard rate (also called the average default intensity) and the spread on debt arelinked by the equation Hazard Rate = Spread/(1 - Recovery Rate). Therefore, the recovery rate implicit in the given data is = 1 - 8%/10% = 20%.
質問 # 151
Which of the following are valid approaches to leveraging external loss data for modeling operational risks:
I. Both internal and external losses can be fitted with distributions,and a weighted average approach using these distributions is relied upon for capital calculations.
II. External loss data is used to inform scenario modeling.
III. External loss data is combined with internal loss data points, and distributions fitted to the combined data set.
IV. External loss data is used to replace internal loss data points to create a higher quality data set to fit distributions.
- A. II and IV
- B. I and III
- C. All of the above
- D. I, II and III
正解:D
解説:
Explanation
Internal loss data isgenerally the highest quality as it is relevant, and is 'real' as it has occurred to the organization. External loss data suffers from a significant limitation that the risk profiles of the banks to which the data relates is generally not known due to anonymization, and may likely may not be applicable to the bank performing the calculations. Therefore, replacing external loss data with external loss data is not a good idea. Statement IV is therefore incorrect.
All other approach described are valid approaches for the risk analyst to consider and implement. Therefore statements I, II and III are correct and IV is not.
質問 # 152
If the cumulative default probabilities of default for years 1 and 2 for a portfolio of credit risky assets is 5% and 15% respectively, what is the marginal probability of default in year 2 alone?
- A. 11.76%
- B. 15.79%
- C. 10.53%
- D. 10.00%
正解:C
解説:
Explanation
One way to think about this question is this: we are provided with two pieces of information: if the portfolio is worth $100 to start with, it will be worth $95 at the end of year 1 and $85 at the end of year 2. What it isasking for is the probability of default in year 2, for the debts that have survived year 1. This probability is $10/$95 =
10.53%. Choice 'b' is the correct answer.
Note that marginal probabilities of default are the probabilities for default for a given period, conditional on survival till the end of the previous period. Cumulative probabilities of default are probabilities of default by a point in time, regardless of when the default occurs. If the marginal probabilities of default for periods 1, 2... n are p1, p2...pn, then cumulative probability of default can be calculated as Cn = 1 - (1 - p1)(1-p2)...(1-pn). For this question, we can calculate the probability of default for year 2 as [1 - (1 - 5%)(1 - 10.53%)] = 15%.
質問 # 153
Which of the following statements are true:
I. The sum of unexpected losses for individual loans in a portfolio is equal to the total unexpected loss for the portfolio.
II. The sum of unexpected losses for individual loans in a portfolio is less than the total unexpected loss for the portfolio.
III. The sum of unexpected losses forindividual loans in a portfolio is greater than the total unexpected loss for the portfolio.
IV. The unexpected loss for the portfolio is driven by the unexpected losses of the individual loans in the portfolio and the default correlation between these loans.
- A. I, II and III
- B. II and IV
- C. III and IV
- D. I and II
正解:C
解説:
Explanation
Unexpected losses (UEL) for individual loans in a portfolio will always sum to greater than the total unexpected loss for the portfolio (unless all the loans are correlatedin such a way that they default together).
This is akin to the 'diversification effect' in market risk, in other words, not all the obligors would default together. So the UEL for the portfolio will always be less than the sum of the UELs for individual loans.
Therefore statement III is true.This 'diversification effect' will be affected by the default correlations between the obligors, in cases where the probability of various obligors defaulting together is low, the UEL for the portfolio would bemuch less than the UEL for the individual loans. Hence statement IV is true.I and II are false for the reasons explained above.
質問 # 154
For a corporate issuer, which of the following can be used to calculate market implied default probabilities?
I. CDS spreads
II. Bond prices
III. Credit rating issued by S&P
IV. Altman's scoring model
- A. I, II and III
- B. II and III
- C. I and II
- D. III and IV
正解:C
解説:
Generally, the probability of default is an input into determining the price of a security. However, if we know the market price of a security, we can back out the probability of default that the market is factoring into pricing that security. Market implied default probabilities are the probabilities of default priced into security prices, and can be determined from both bond prices and CDS spreads. Credit ratings issued by a credit agency do not give us 'market implied default probabilities', and neither does an internal scoring model like Altman's as these do not consider actual market prices in any way.
Therefore Choice 'b' is the correct answer and the others are not.
質問 # 155
......
PRMIA 8010 資格認定は、少なくとも2年間の運用リスク管理の経験を持つ専門家を対象としています。この認定プログラムは3つのレベルに分かれており、各レベルは前のレベルで習得した知識とスキルを基盤に構築されています。プログラムの最初のレベルは運用リスク管理の基礎をカバーし、二番目のレベルはモデリングや運用リスクの測定などの高度なトピックに焦点を当てています。プログラムの第三レベルは、前の2つのレベルで習得した知識とスキルを実世界のシナリオに適用できるかどうかを評価するために設計されています。
PRMIA 8010:運用リスクマネージャー(ORM)試験では、それぞれが運用リスク管理に関する候補者の実際的な知識をテストするように設計された複数選択の質問で構成されています。この試験では、エンタープライズ全体のリスク管理、主要なリスク指標、リスクガバナンスと管理システム、運用リスクモデリングと測定技術、および運用リスクを識別および評価するための戦略などのトピックをカバーしています。
8010試験問題集簡単なまとめ:https://www.jpntest.com/shiken/8010-mondaishu
