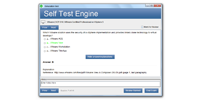
ダウンロード可能なインタラクティブ8010テストエンジン
PRM Certificationの基礎準備資料問題集には、PRM Certification 8010試験を受けるために必要なすべての材料が含まれています。詳細は、正確で論理的なものを作成するために業界の経験を常に使用しているPRM Certification によって研究と構成されています。
JPNTestでPRMIA 8010問題集をチョイスする理由
JPNTestは、1週間で完璧に認定試験を準備することができる、忙しい受験者に最適な問題集を提供しております。 8010の問題集は、PRMIAの専門家チームがベンダーの推奨する授業要綱を深く分析して作成されました。弊社の8010学習材料を一回のみ使用するだけで、PRMIA認証試験に合格することができます。
8010はPRMIAの重要な認証であり、あなたの専門スキルを試す認定でもあります。受験者は、試験を通じて自分の能力を証明したいと考えています。 JPNTest Operational Risk Manager (ORM) Exam は、PRM Certificationの242の問題と回答を収集して作成しました。Operational Risk Manager (ORM) Examの知識ポイントをカバーし、候補者の能力を強化するように設計されています。 JPNTest 8010受験問題集を使用すると、Operational Risk Manager (ORM) Examに簡単に合格し、PRMIA認定を取得して、PRMIAとしてのキャリアをさらに歩むことができます。
あなたの8010試験合格を100%保証
JPNTestテスト問題集を初めて使用したときにPRM Certification 8010試験(Operational Risk Manager (ORM) Exam)に合格されなかった場合は、購入料金を全額ご返金いたします。
8010試験の品質と価値
JPNTestのPRM Certification 8010模擬試験問題集は、認定された対象分野の専門家と公開された作成者のみを使用して、最高の技術精度標準に沿って作成されています。
8010の迅速なアップデート対応
8010試験に変更がございました場合は、現在の試験と一致するよう、瞬時に学習資料を更新することができます。弊社は、お客様に最高、最新のPRMIA 8010問題集を提供することに専念しています。なお、ご購入いただいた製品は365日間無料でアップデートされます。
PRMIA Operational Risk Manager (ORM) 認定 8010 試験問題:
1. The largest 10 lossesover a 250 day observation period are as follows. Calculate the expected shortfall at a
98% confidence level:
20m
19m
19m
17m
16m
13m
11m
10m
9m
9m
A) 18.2
B) 19.5
C) 16
D) 14.3
2. Once the frequency and severity distributions for loss events have been determined, which of the following is an accurate description of the process to determine a full loss distribution for operational risk?
A) The frequency distribution alone forms the basis for the loss distribution for operational risk
B) A firm wide operational risk distribution is generated by adding together the frequency and severity distributions
C) A firm wide operational risk distribution is generated using Monte Carlo simulations
D) A firm wide operational risk distribution is set to be equal to the product of the frequency and severity distributions
3. For a given mean, which distribution would you prefer for frequency modeling where operational risk events are considered dependent, or in other words are seen as clustering together (as opposed to being independent)?
A) Gamma
B) Poisson
C) Negative binomial
D) Binomial
4. The probability of default of a security during the first year after issuance is 3%, that during the second and third years is 4%, and during the fourth year is 5%. What is the probability that it would not have defaulted at the end of four years from now?
A) 12.00%
B) 84.93%
C) 88.00%
D) 88.53%
5. Which of the following is not a limitation of the univariate Gaussian model to capture the codependence structure between risk factros used for VaR calculations?
A) The univariate Gaussian model fails to fit to the empirical distributions of risk factors, notably their fat tails and skewness.
B) Determining the covariance matrix becomes an extremely difficult task as the number of risk factors increases.
C) A single covariance matrix is insufficient to describe the fine codependence structure among risk factors as non-linear dependencies or tail correlations are not captured.
D) It cannot capture linear relationships between risk factors.
質問と回答:
| 質問 # 1 正解: A | 質問 # 2 正解: C | 質問 # 3 正解: C | 質問 # 4 正解: B | 質問 # 5 正解: D |


 313 お客様のコメント
313 お客様のコメント